
This number changes often, so investors sometimes use the weighted average of the shares outstanding to determine the EPS for a specific time period. For example, they may compare the forward EPS (that uses projections) with the company’s actual EPS for the current quarter. If the actual EPS falls short of forward EPS projections, the stock price may fall as investors register their disappointment. create custom invoice templates using our free invoice generator EPS is typically used by investors and analysts to gauge the financial strength of a company. In fact, it is sometimes known as the bottom line where a firm’s worth is concerned, both literally (as the last item on the income statement) and figuratively. Diluted EPS, which accounts for the impact of convertible preferred shares, options, warrants, and other dilutive securities, was $1.56.
A Variable in the Price/Earning Ratio
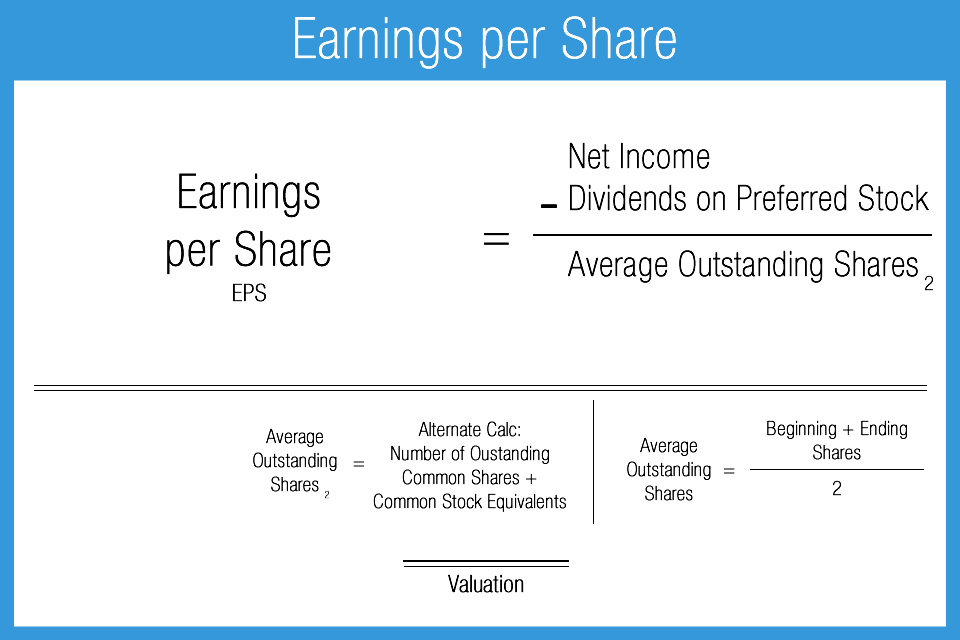
The resulting EPS tells you how much a company is earning for each outstanding share of stock. By providing a common base metric, EPS makes it easier to compare companies, each of which has a different number of outstanding shares, stock price and profits. To find EPS, take the company’s net income (and deduct preferred dividends, if applicable) and divide that by the average number of shares of outstanding common stock. Basic earnings per share is a rough measurement of the amount of a company’s profit that can be allocated to one share of its common stock. Businesses with simple capital structures, where only common stock has been issued, need only release this ratio to reveal their profitability. Basic earnings per share does not factor in the dilutive effects of convertible securities.
Why Is Earnings per Share (EPS) Important to Investors? FAQs
- If a company can quickly grow its EPS, then its stock will likely rise.
- A company with a steadily increasing EPS figure is considered to be a more reliable investment than one whose EPS is on the decline or varies substantially.
- Furthermore, EPS serves as a useful comparative tool, enabling investors to measure the profitability of different companies and facilitating better-informed decisions regarding portfolio diversification.
- Likewise, a shrinking EPS figure might nonetheless lead to a price increase if analysts were expecting an even worse result.
EPS is a market multiple ratio, meaning it simplifies financial statements into a number that can be compared to peers. However, the diluted figure is generally better and more comprehensive when making investment decisions. Earnings per share, or EPS, is a simple calculation that shows how much profit a company can generate per share of its stock.
Example of EPS
Rolling EPS gives an annual earnings per share (EPS) estimate by combining EPS from the past two quarters with estimated EPS from the next two quarters. Earnings per share can be distorted, both intentionally and unintentionally, by several factors. Analysts use variations of the basic EPS formula to avoid the most common ways that EPS may be inflated. Sometimes an adjustment to the numerator is required when calculating a fully diluted EPS. For example, sometimes a lender will provide a loan that allows them to convert the debt into shares under certain conditions. If you have an interest in stock trading or investing, your next step is to choose a broker that works for your investment style.
How is EPS reported?
Over time, it became clear that the dotcoms weren’t going to make nearly as much money as many had predicted. It simply wasn’t possible for the market to support these companies’ high valuations without any earnings; as a result, the stock prices of these companies collapsed. Diluted EPS also accounts for other kinds of securities that can be converted into common shares, such as employee stock options and convertible bonds. But, you need to know that the additional shares that can become outstanding will also be included as common stock. This can be for a number of reasons, including being part of the compensation plans of the company or as convertible debt/common stock. Earnings per share, or EPS, is a ratio that divides a company’s earnings by the number of shares outstanding to evaluate profitability and gain a pulse of the company’s financial health.
Since we now have the beginning and ending number of common shares outstanding, the next step is to calculate the weighted average shares outstanding. If it loses $10 million with 10 million shares outstanding, basic loss per share is $1.00 even. But the outstanding options — whether in the money or not — do not affect diluted share count. Again, they are anti-dilutive; if they were added to the diluted share count, loss per share would improve slightly, to $0.95. To calculate a company’s earnings per share, divide total earnings by the number of outstanding shares.
If earnings decrease or the number of shares increases, EPS will decline as well. Changes to accounting policy for reporting earnings can also change EPS. EPS also does not take into account the price of the share, so it has little to say about whether a company’s stock is over or undervalued. Earnings forecasts are based on educated guesswork from analysts and are often too rosy, possibly making the valuation look cheap.
In other words, this is the amount of money each share of stock would receive if all of the profits were distributed to the outstanding shares at the end of the year. Typically, an average number is used because companies may issue or buy back stock throughout the year and that makes the actual outstanding shares and true earnings per share difficult to pin down. Using an average of outstanding shares can provide an accurate picture of the earnings for the company.
$3 per share in EPS would be impressive if the company earned only $1 per share the year before. Nevertheless, it’s important not to limit your fundamental stock research only to EPS, as other metrics should be evaluated as well to generate a well-rounded assessment. But even though they’re different measures, these ratios are connected. On the other hand, EPS is an easy-to-calculate, readily available way to interpret how much profit a company makes per share. In such cases, the company may be investing heavily in expenses like R&D to grow.
The answer to “what is a good EPS” for a particular stock depends on what you’re trying to do — and on the industry that stock operates in. Basic EPS, as the name implies, is the simpler way of calculating EPS, and only uses outstanding shares of common stock in the calculation. Another consideration for basic EPS is its deviation from diluted EPS. If the two EPS measures are increasingly different, it may show that there is a high potential for current common shareholders to be diluted in the future. Companies with a complex capital structure must report both basic EPS and diluted EPS to provide a more accurate picture of their earnings.

Recent Comments